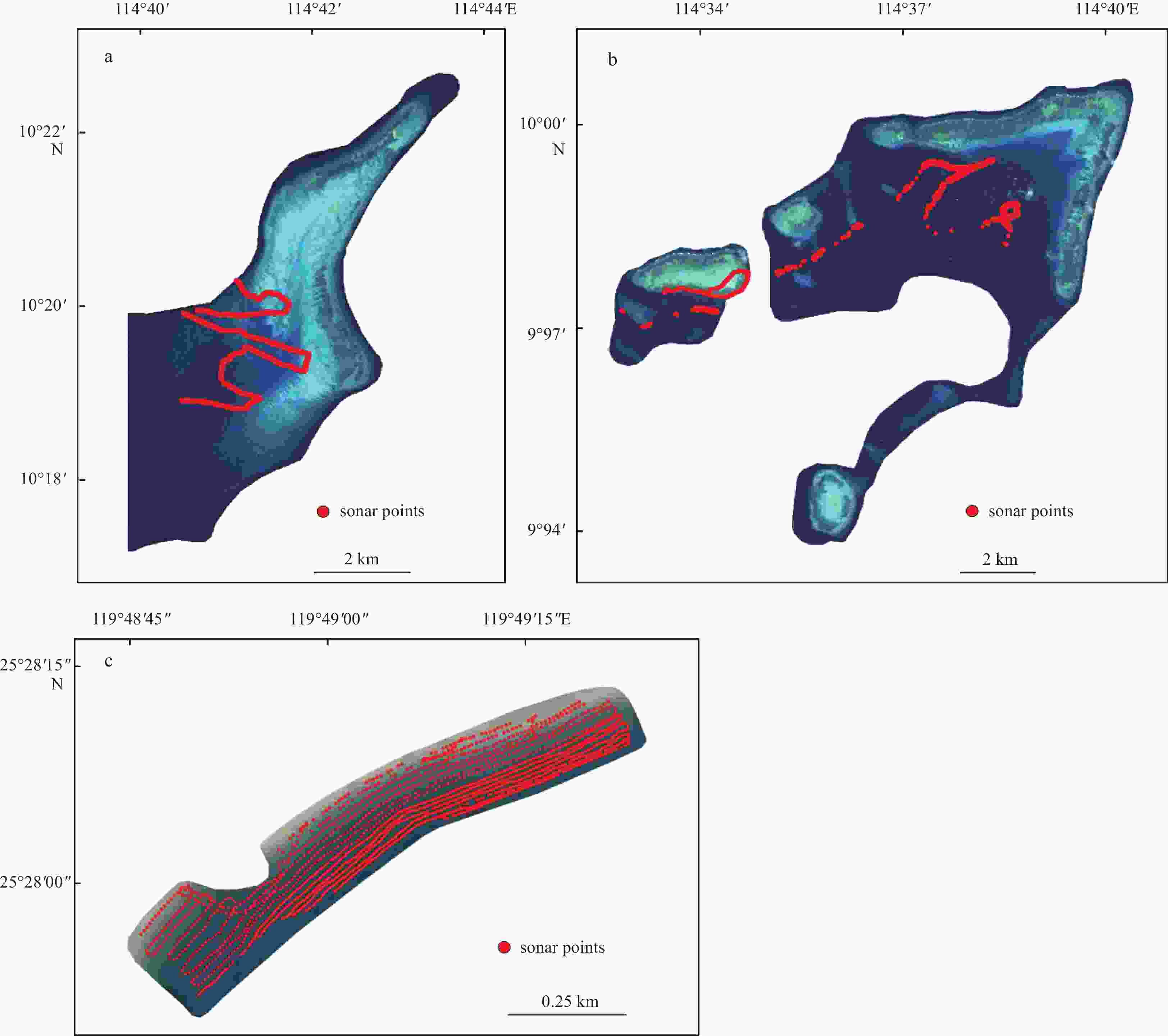
Shallow water bathymetry based on a back propagation neural network and ensemble learning using multispectral satellite imagery
-
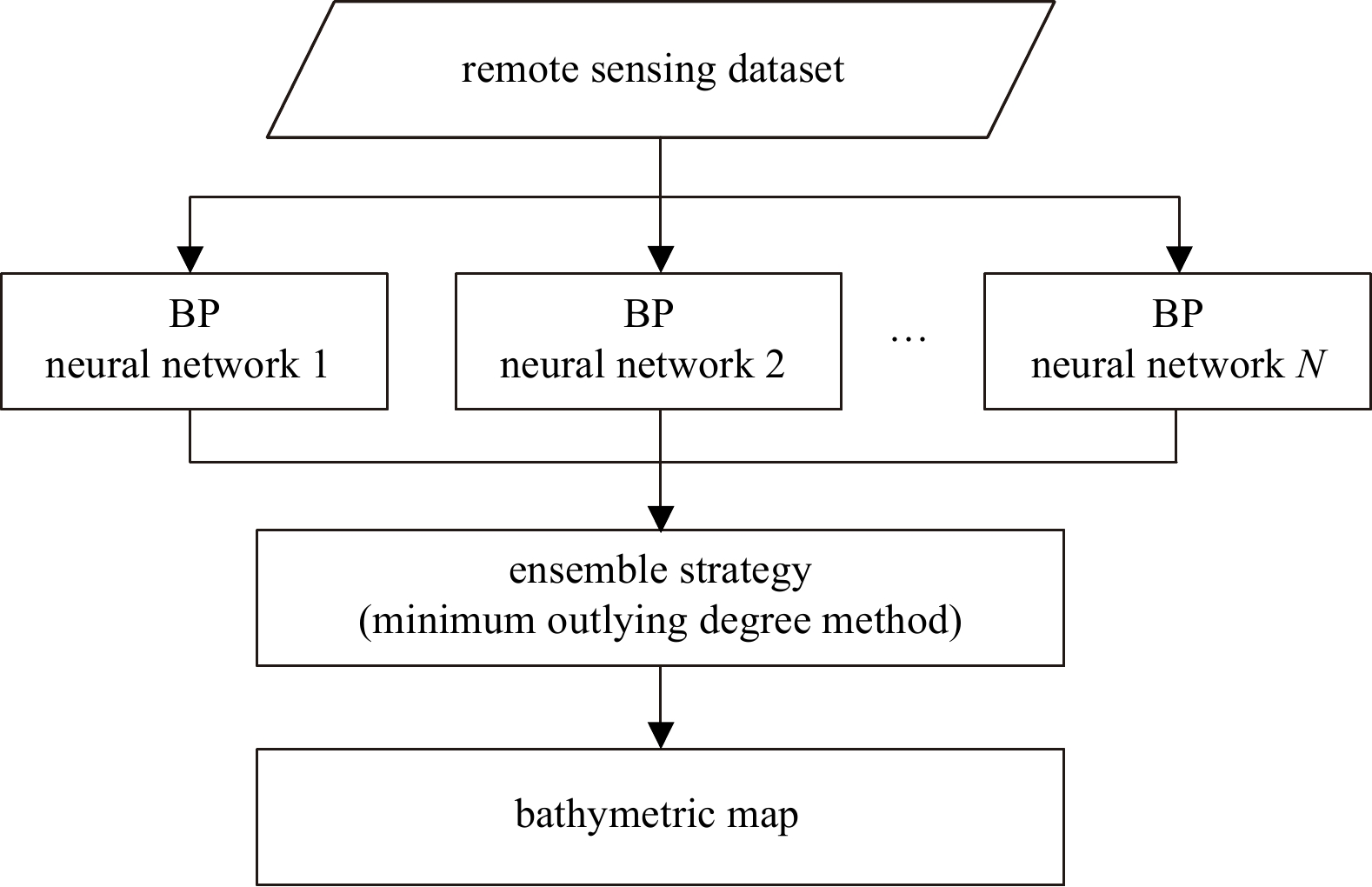
Abstract: The back propagation (BP) neural network method is widely used in bathymetry based on multispectral satellite imagery. However, the classical BP neural network method faces a potential problem because it easily falls into a local minimum, leading to model training failure. This study confirmed that the local minimum problem of the BP neural network method exists in the bathymetry field and cannot be ignored. Furthermore, to solve the local minimum problem of the BP neural network method, a bathymetry method based on a BP neural network and ensemble learning (BPEL) is proposed. First, the remote sensing imagery and training sample were used as input datasets, and the BP method was used as the base learner to produce multiple water depth inversion results. Then, a new ensemble strategy, namely the minimum outlying degree method, was proposed and used to integrate the water depth inversion results. Finally, an ensemble bathymetric map was acquired. Anda Reef, northeastern Jiuzhang Atoll, and Pingtan coastal zone were selected as test cases to validate the proposed method. Compared with the BP neural network method, the root-mean-square error and the average relative error of the BPEL method can reduce by 0.65–2.84 m and 16%–46% in the three test cases at most. The results showed that the proposed BPEL method could solve the local minimum problem of the BP neural network method and obtain highly robust and accurate bathymetric maps.
-
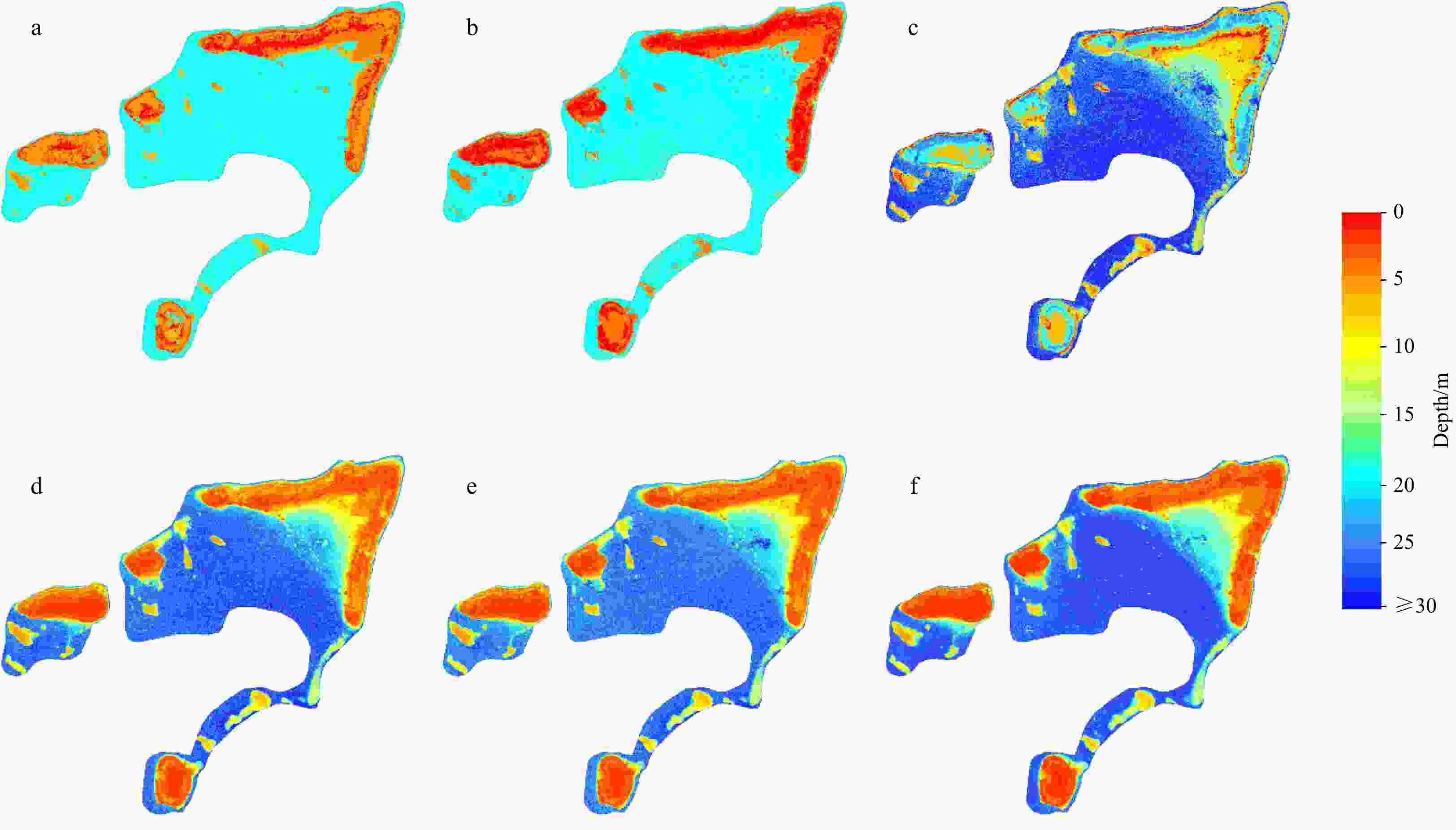
Figure 5. Bathymetric maps of the three worst results for the back propagation (BP) and BP neural network and ensemble learning (BPEL) methods in the Anda Reef. a–c. Bathymetric maps of the 85th, 31st, and 91st repeated experiments for the BP method. d–f. Bathymetric maps of the 50th, 70th, and 96th repeated experiments for the BPEL method.
Figure 6. Scatterplots (estimated depth versus measured depth) of the three worst results for the back propagation (BP) and BP neural network and ensemble learning (BPEL) methods in the Anda Reef. a–c. Scatterplots of the 85th, 31st, and 91st repeated experiments for the BP method. d–f. Scatterplots of the 50th, 70th, and 96th repeated experiments for the BPEL method.
Figure 7. Bathymetric maps of the three worst results for the back propagation (BP) and BP neural network and ensemble learning (BPEL) methods in the northeastern Jiuzhang Atoll. a–c. Bathymetric maps of the 57th, 72nd, and 91st repeated experiments for the BP method. d–f. Bathymetric maps of the 96th, 58th, and 8th repeated experiments for the BPEL method.
Figure 8. Scatterplots (estimated depth versus measured depth) of the three worst results for the back propagation (BP) and BP neural network and ensemble learning (BPEL) methods in the northeastern Jiuzhang Atoll. a–c. Scatterplots of the 57th, 72nd, and 91st repeated experiments for the BP method. d–f. Scatterplots of the 96th, 58th, and 8th repeated experiments for the BPEL method.
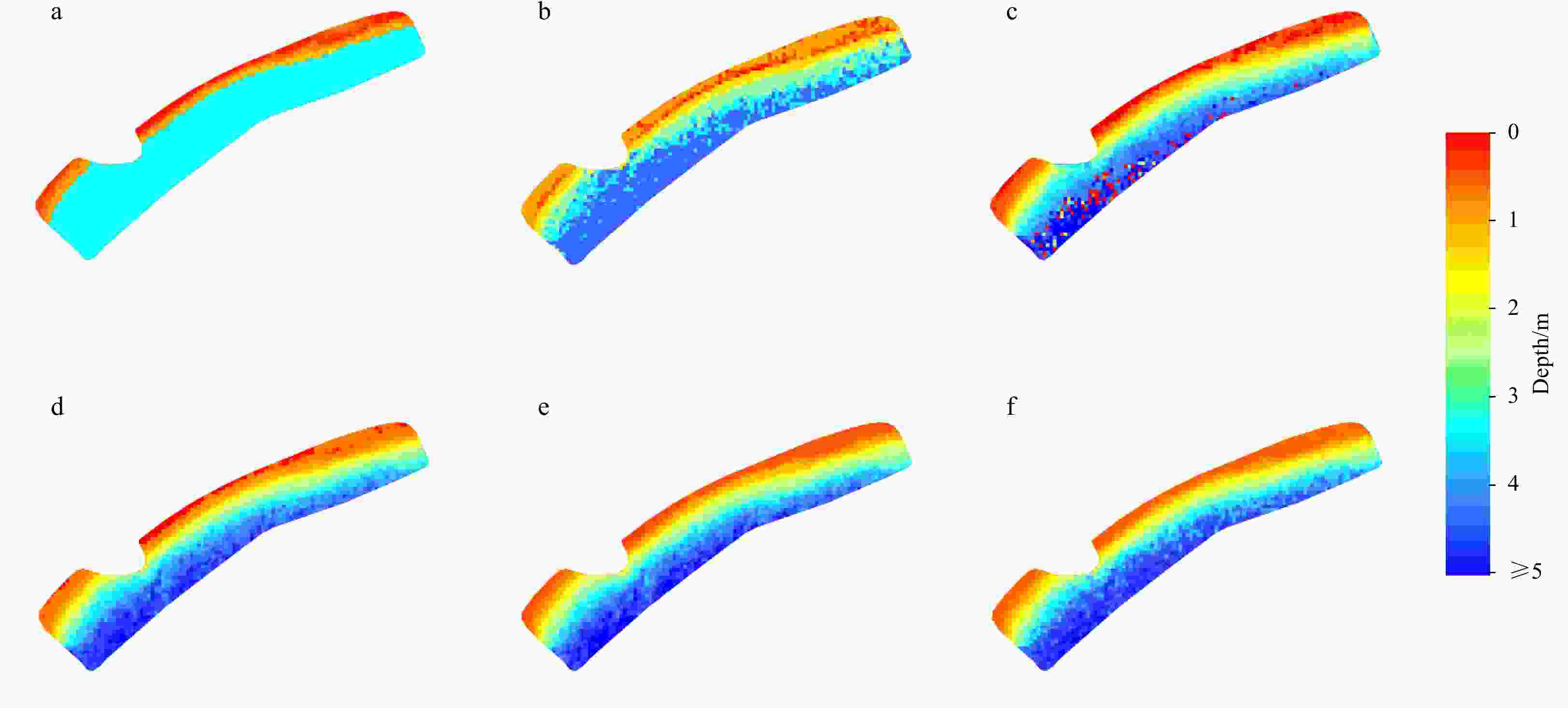
Figure 9. Bathymetric maps of the three worst results for the back propagation (BP) and BP neural network and ensemble learning (BPEL) methods in the Pingtan coastal zone. a–c. Bathymetric maps of the 41st, 39th, and 45th repeated experiments for the BP method. d–f. Bathymetric maps of the 43rd, 74th, and 59th repeated experiments for the BPEL method.
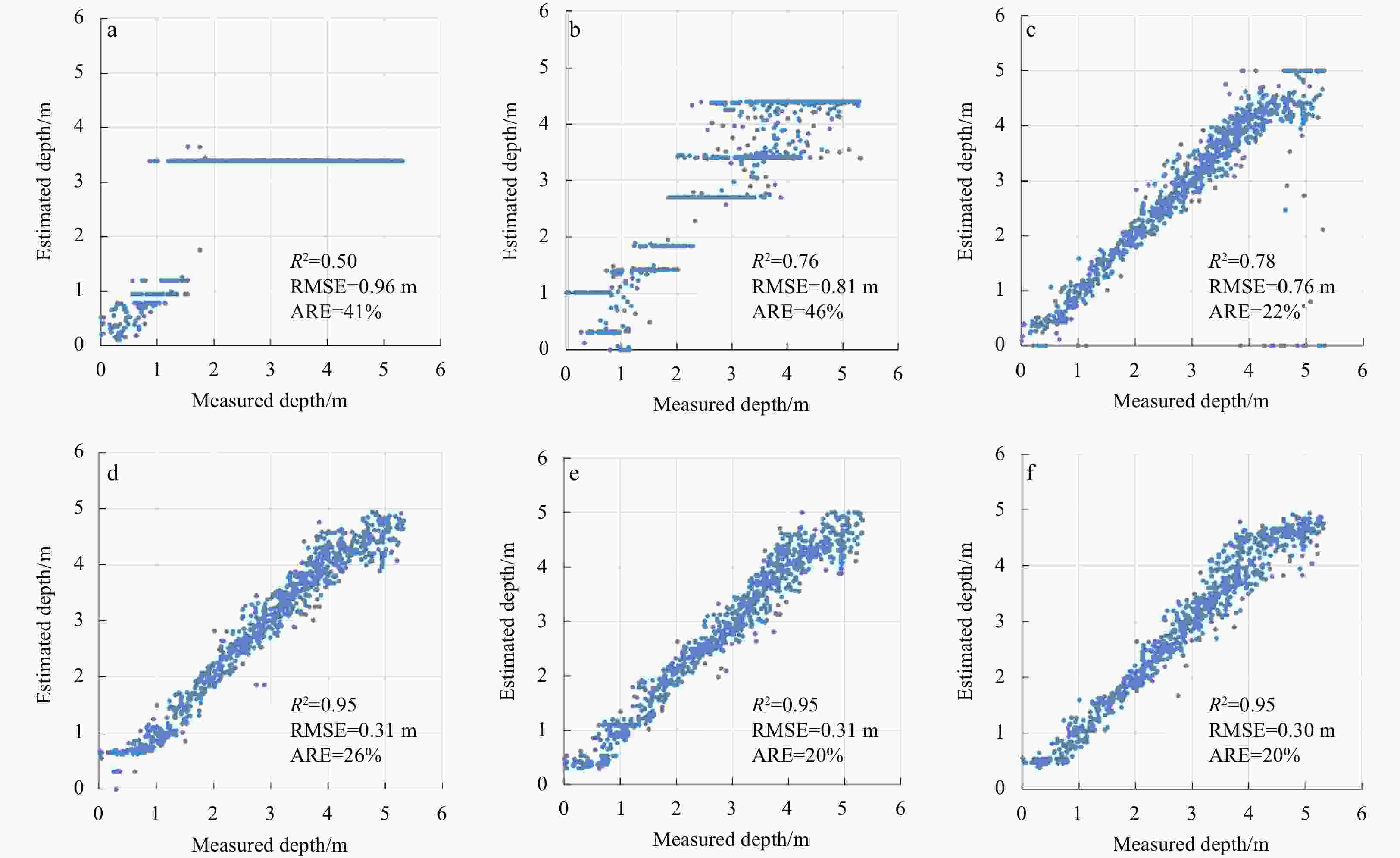
Figure 10. Scatterplots (estimated depth versus measured depth) of the three worst results for the back propagation (BP) and BP neural network and ensemble learning (BPEL) methods in the Pingtan coastal zone. a–c. Scatterplots of the 41st, 39th, and 45th repeated experiments for the BP method. d–f. Scatterplots of the 43rd, 74th, and 59th repeated experiments for the BPEL method.
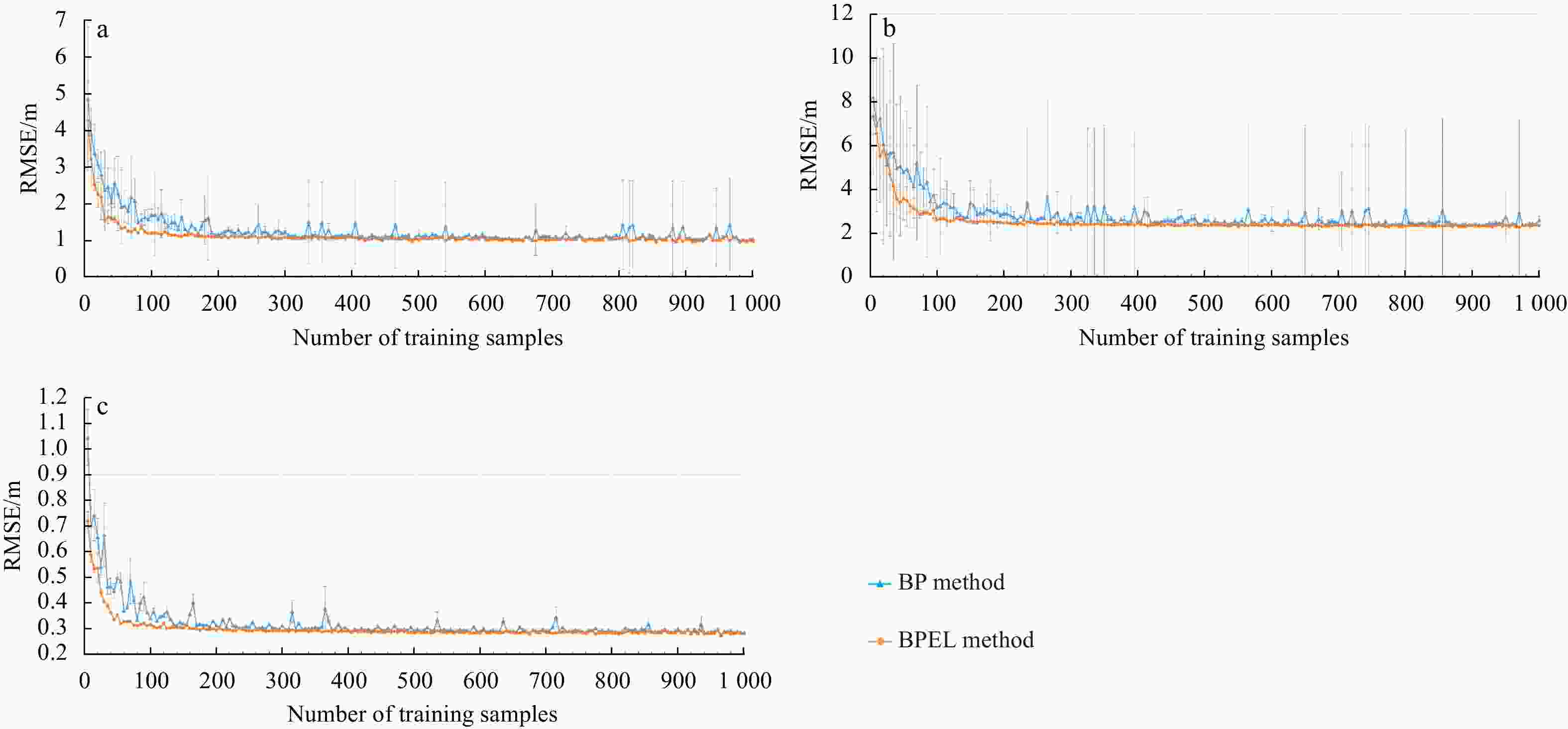
Figure 11. Effects of the number of training samples on the accuracy of back propagation (BP) and BP neural network and ensemble learning (BPEL) methods. RMSE of bathymetric inversion experiments in the Anda Reef (a), northeastern Jiuzhang Atoll (b), and Pingtan coastal zone (c). Error bars are the standard deviation of the RMSE values.
Figure 12. Effects of the number of base learners on the accuracy of BP neural network and ensemble learning (BPEL) methods. RMSE of bathymetric inversion experiments in the Anda Reef (a), northeastern Jiuzhang Atoll (b), and Pingtan coastal zone (c). Error bars are the standard deviation of the RMSE values. The blue point and line in L=1 are the RMSE and error bar of the back propagation (BP) methods.
Table 1. Comparison of inversion accuracies (RMSEs) of the three worst results of the back propagation (BP) and BP neural network and ensemble learning (BPEL) methods
Study area Water
depth/mN BP BPEL Worst result Second worst result Third worst result Worst result Second worst result Third worst result Anda Reef 0–5 180 1.87 2.17 2.32 1.59 1.58 1.66 5–10 386 2.99 1.96 1.33 0.92 0.93 0.88 10–15 324 1.39 1.56 1.65 0.85 0.95 0.89 15–20 125 5.41 3.56 3.76 1.35 1.20 1.31 Overall 1 025 2.91 2.22 2.13 1.15 1.14 1.14 Northeastern
Jiuzhang Atoll0–5 150 5.07 2.73 10.09 0.84 0.77 0.85 5–10 145 5.84 7.88 2.05 1.73 1.51 1.62 10–15 73 7.54 7.79 4.02 3.26 2.98 3.42 15–20 285 3.14 3.08 4.38 2.96 2.52 3.03 20–25 187 2.98 2.67 4.4 2.27 2.04 2.62 25–30 181 8.01 7.32 3.49 3.28 3.91 2.48 Overall 1 021 5.39 5.35 5.33 2.55 2.53 2.53 Pingtan
coastal zone0–1 104 0.47 0.56 0.26 0.25 0.23 0.21 1–2 135 1.44 0.47 0.29 0.20 0.22 0.15 2–3 181 0.92 0.82 0.27 0.26 0.21 0.24 3–4 256 0.37 0.69 0.39 0.27 0.31 0.35 4–5 209 1.27 0.83 1.13 0.41 0.41 0.36 Overall 885 0.96 0.81 0.76 0.31 0.31 0.30 Note: N represents the number of test samples. -
Andréfouët S, Kramer P, Torres-Pulliza D, et al. 2003. Multi-site evaluation of IKONOS data for classification of tropical coral reef environments. Remote Sensing of Environment, 88(1–2): 128–143, Andrejev O, Soomere T, Sokolov A, et al. 2011. The role of the spatial resolution of a three-dimensional hydrodynamic model for marine transport risk assessment. Oceanologia, 53(S1): 309–334. doi: 10.5697/oc.53-1-TI.309 Benardos P G, Vosniakos G C. 2007. Optimizing feedforward artificial neural network architecture. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 20(3): 365–382. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2006.06.005 Cao Bincai, Fang Yong, Gao Li, et al. 2021. An active-passive fusion strategy and accuracy evaluation for shallow water bathymetry based on ICESat-2 ATLAS laser point cloud and satellite remote sensing imagery. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 42(8): 2783–2806. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2020.1862441 Casal G, Monteys X, Hedley J, et al. 2019. Assessment of empirical algorithms for bathymetry extraction using Sentinel-2 data. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 40(8): 2855–2879. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2018.1533660 Ceyhun Ö, Yalçın A. 2010. Remote sensing of water depths in shallow waters via artificial neural networks. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 89(1): 89–96, Chu Sensen, Cheng Liang, Ruan Xiaoguang, et al. 2019. Technical framework for shallow-water bathymetry with high reliability and no missing data based on time-series Sentinel-2 images. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 57(11): 8745–8763. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2922724 Collin A, Etienne S, Feunteun E. 2017. VHR coastal bathymetry using WorldView-3: colour versus learner. Remote Sensing Letters, 8(11): 1072–1081. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2017.1354261 Deng Ying, Zhou Xiaoling, Shen Jiao, et al. 2021. New methods based on back propagation (BP) and radial basis function (RBF) artificial neural networks (ANNs) for predicting the occurrence of haloketones in tap water. Science of The Total Environment, 772: 145534. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145534 El-Mewafi M, Salah M, Fawzi B. 2018. Assessment of optical satellite images for bathymetry estimation in shallow areas using artificial neural network model. Journal of Geographic Information System, 7(4): 99–106. doi: 10.5923/j.ajgis.20180704.01 Gholamalifard M, Kutser T, Esmaili-Sari A, et al. 2013. Remotely sensed empirical modeling of bathymetry in the southeastern Caspian Sea. Remote Sensing, 5(6): 2746–2762. doi: 10.3390/rs5062746 Guo Hengliang, Yang Hong, Qiao Baojin, et al. 2021. Multi-resolution satellite images bathymetry inversion of Bangda Co in the western Tibetan Plateau. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 42(21): 8077–8098. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2021.1970271 Hirose Y, Yamashita K, Hijiya S. 1991. Back-propagation algorithm which varies the number of hidden units. Neural Networks, 4(1): 61–66. doi: 10.1016/0893-6080(91)90032-Z Huang Rongyong, Yu Kefu, Wang Yinghui, et al. 2017. Bathymetry of the coral reefs of Weizhou Island based on multispectral satellite images. Remote Sensing, 9(7): 750. doi: 10.3390/rs9070750 Hussein H M, Nadaoka K. 2017. Assessment of machine learning approaches for bathymetry mapping in shallow water environments using multispectral satellite images. International Journal of Geoinformatics, 13(2): 1–15 Islam M M, Yao Xin, Murase K. 2003. A constructive algorithm for training cooperative neural network ensembles. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 14(4): 820–834. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2003.813832 Kim J S, Baek D, Seo II W, et al. 2019. Retrieving shallow stream bathymetry from UAV-assisted RGB imagery using a geospatial regression method. Geomorphology, 341: 102–114. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2019.05.016 Lee Zhongping, Carder K L, Mobley C D, et al. 1998. Hyperspectral remote sensing for shallow waters. I. A semianalytical model. Applied Optics, 37(27): 6329–6338. doi: 10.1364/AO.37.006329 Lee Y, Oh S H, Kim M W. 1993. An analysis of premature saturation in back propagation learning. Neural Networks, 6(5): 719–728. doi: 10.1016/S0893-6080(05)80116-9 Leon J X, Cohen T J. 2012. An improved bathymetric model for the modern and Palaeo Lake Eyre. Geomorphology, 173–174: 69–79, Li Jing, Cheng Jihang, Shi Jingyuan, et al. 2012. Brief introduction of back propagation (BP) neural network algorithm and its improvement. In: Jin D, Lin S, eds. Advances in Computer Science and Information Engineering. Berlin: Springer, 553–558, Liang Jian, Zhang Jie, Ma Yi. 2017. A spatial resolution effect analysis of remote sensing bathymetry. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 36(7): 102–109. doi: 10.1007/s13131-017-1088-x Liu Shan, Gao Yong, Zheng Wenfeng, et al. 2015. Performance of two neural network models in bathymetry. Remote Sensing Letters, 6(4): 321–330. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2015.1034885 Liu Shan, Wang Lei, Liu Hongxing, et al. 2018. Deriving bathymetry from optical images with a localized neural network algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 56(9): 5334–5342. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2814012 Lyzenga D R. 1978. Passive remote sensing techniques for mapping water depth and bottom features. Applied Optics, 17(3): 379–383. doi: 10.1364/ao.17.000379 Lyzenga D R. 1985. Shallow-water bathymetry using combined lidar and passive multispectral scanner data. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 6(1): 115–125. doi: 10.1080/01431168508948428 Ma Yue, Xu Nan, Liu Zhen, et al. 2020. Satellite-derived bathymetry using the ICESat-2 lidar and sentinel-2 imagery datasets. Remote Sensing of Environment, 250: 112047. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2020.112047 Manessa M D M, Kanno A, Sagawa T, et al. 2018. Simulation-based investigation of the generality of Lyzenga’s multispectral bathymetry formula in Case-1 coral reef water. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 200: 81–90, Melet A, Teatini P, Le Cozannet G, et al. 2020. Earth observations for monitoring marine coastal hazards and their drivers. Surveys in Geophysics, 41(6): 1489–1534. doi: 10.1007/s10712-020-09594-5 Polcyn F C. 1976. NASA/Cousteau ocean bathymetry experiment. NASA CR-ERIM 118500-l-F. Ann Arbor, MI: Environmental Research Institute of Michigan Qiu Luo, Zhang Dexian, Huang Hao, et al. 2018. BP artificial neural network and its application based on LM algorithm. NeuroQuantology, 16(6): 598–605. doi: 10.14704/nq.2018.16.6.1566 Rumelhart D E, McClelland J L. 1986. Parallel Distributed Processing: Explorations in the Microstructure of Cognition. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press Sandidge J C, Holyer R J. 1998. Coastal bathymetry from hyperspectral observations of water radiance. Remote Sensing of Environment, 65(3): 341–352. doi: 10.1016/S0034-4257(98)00043-1 Stumpf R P, Holderied K, Sinclair M. 2003. Determination of water depth with high-resolution satellite imagery over variable bottom types. Limnology and Oceanography, 48(1): 547–556. doi: 10.4319/lo.2003.48.1_part_2.0547 Sun Minxuan, Yu Linjun, Zhang Ping, et al. 2021. Coastal water bathymetry for critical zone management using regression tree models from Gaofen-6 imagery. Ocean & Coastal Management, 204: 105522. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2021.105522 Wang Yanhong, Zhou Xinghua, Li Cong, et al. 2020. Bathymetry model based on spectral and spatial multifeatures of remote sensing image. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 17(1): 37–41. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2915122 -




 下载:
下载: